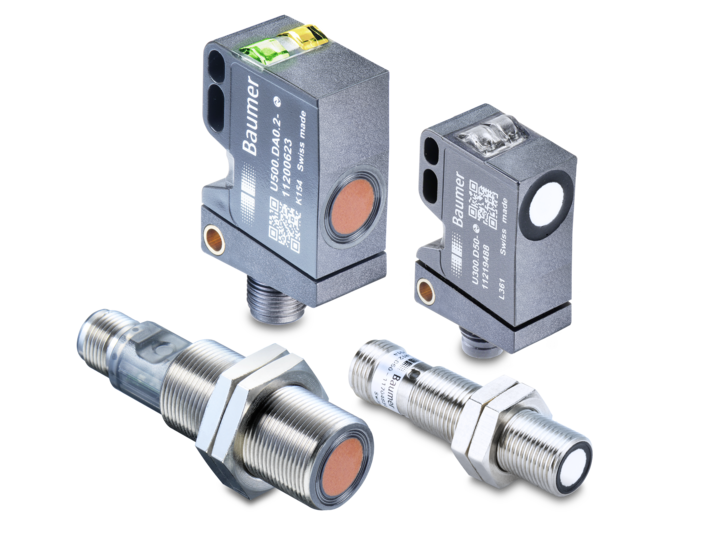
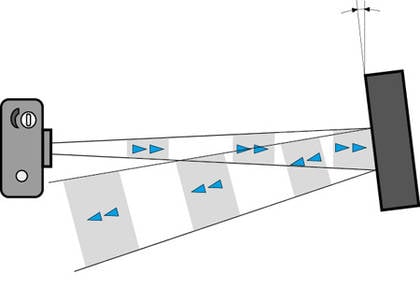
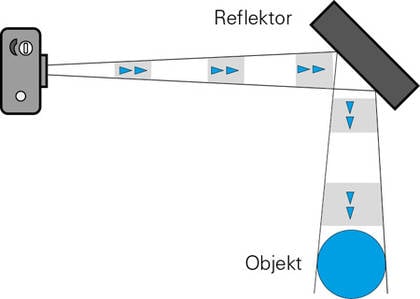
Baumer ultrasonic sensors offer a high degree of flexibility in installation. The only prerequisite during mounting is to ensure that no materials can settle in the area of the sonic beam. Soundabsorbing materials such as cotton wool or soft foam rubber can reduce the scanning range. Liquids and solid materials are very good reflectors of sound.
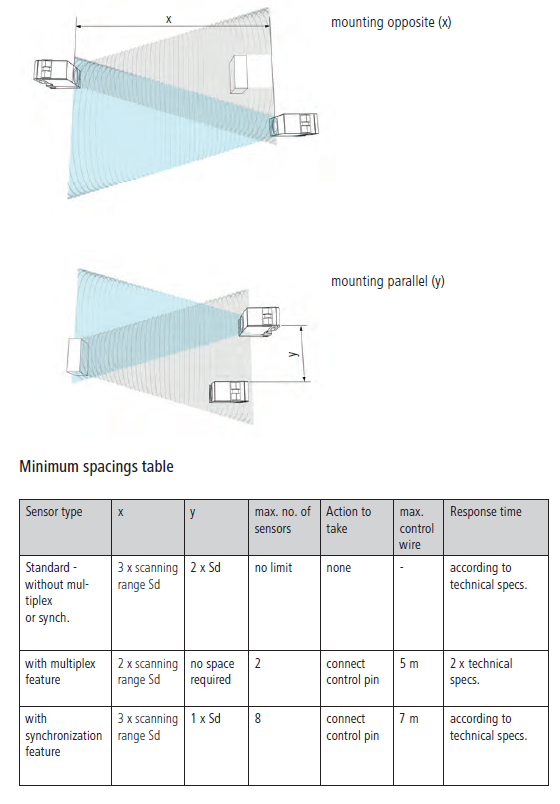
Minimum spacings
To avoid mutual influencing of the sensors, depending on the type of sensor, a specific spacing must be maintained between the sensors:
Synchronization or Multiplex feature
Minimum spacing cannot always be maintained in all applications. Sensors with synchronization mode are used for this purpose. Such sensors synchronize the transfer cycles of the individual sensors with the aim of reducing the minimum spacing.
Synchronization feature
Link the control pin of all sensors within a limited area to each other. This triggers the measurement of all sensors at the same time. Interference signals which arrive later at the sensor due to their longer sensing distance, will be ignored. Up to eight sensors can be synchronized via control pin.
Multiplex feature
Link the control pin of both sensors to each other. While the first sensor is measuring, the second is disabled. After the first measurement is completed, the second sensor is allowed to send and receive its signals. In maximum two sensors can be interconnected. The multiplex function increases the sensor response time to the double of the specified value.
Note: The control pin must be closed on sensors utilizing either the synchronization or multiplex feature. If the feature is not in use the pin must be connected to the following potentials to ensure the standard response time:
- Synchronization: Connect the control pin to supply voltage (+Vs)
- Multiplex: Connect the control pin to ground (GND)
Adjustment aid
The LED indicates the intensity of the signal which has been reflected by the object, as well as the output's switching state.
- LED on
The object is reliably detected with a signal strength reserve of 50 %. The output is switched.
- LED off
No target detected, output is not switched.
- LED flashing
Unreliable detection of the target. The output is activated / switched.
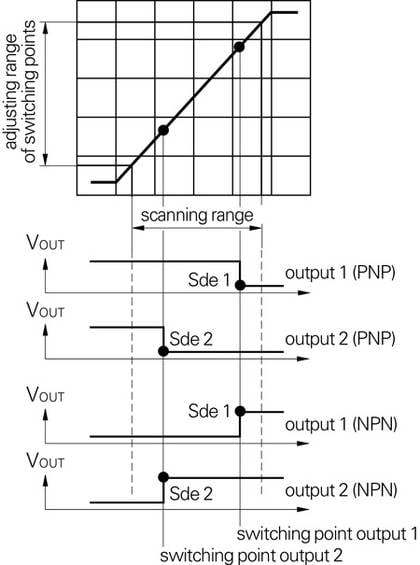
Teach-in
Ultrasonic sensors with the "Teach-in" function are similar to the standard range of products but have the added versatility of a simple touch key set up. The switching points (Sde 1 and Sde 2) may be easily programmed within the sensing range by means of the built-in Teach-in button.
General Settings
- Teach-in lock
The Teach-in lock is active 5 minutes after power-up or after the end of the last Teach-in process. Teach-in lock is reset by disconnecting the power supply. The Teach-in lock can be released by briefly switching the main power off.
- Resetting to original factory settings
Holding the button down for > 6 secs, will automatically restore the original factory setting. Fast flashing of the green/yellow LED indicates successful completion of the resetting.
Setting of Ultrasonic proximity switches
The switching points (Sde 1 and Sde 2) may be easily programmed within the sensing range by means of the built-in Teach-in button.
Functional diagram
Setting of utrasonic retro-reflectiv sensors
Setting Sde reflector distance
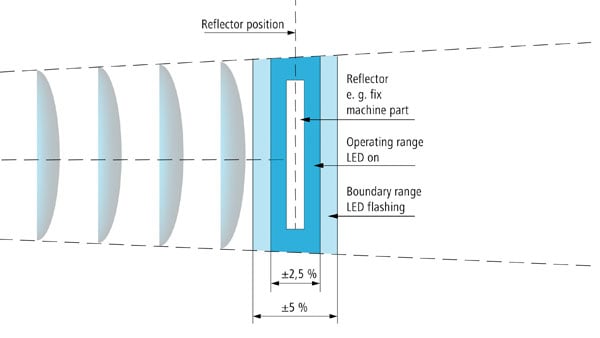
The sensor's potentiometer allows the user to adjust the set up conditions for a specific reflector position (Sde). The output LED is also an adjustment aid as follows:
- 1. Reflector in operating range
If the setting of Sde deviates from the actual reflector position by less than ±2,5 %, the reflector is in the operating range. The LED lights steadily, the output is inactive.
- 2. Reflector in the boundary range
Up to a deviation of ±5 % the output remains inactive but the LED flashes. This indicates that the setting of Sde is not optimal and needs to be corrected.
All adjustments are made using the single built-in Teach-in button.
Teach-in of reflector’s position
To enter the adjustment mode, push the Teach-in button for more than two seconds. You will know you have pushed it long enough by the indicating LED flashing green. When the button is released, the LED continues to flash. Any subsequent push of the button will teach the position of the reflector.
Settings of ultrasonic through beam sensors
All adjustments can be made with the internal Teach-in key.
Sensitivity Adjustment
The LEDs on the display indicate the receiver’s sensitivity. The sensitivity can be called up at any time by pressing the Teach-in key, even with locked teaching functionality.
Move the emitter and receiver to the desired position.
Switch the emitter to its adjustment mode by pressing and holding the Teach-in key for approx. two seconds until the green LED begins flashing. Release the Teach-in key. The green LED now indicates the switching state. Press the Teach-in key repeatedly until the desired sensitivity is achieved and the green LED is continuously on.
Sensitivity is indicated by the yellow LEDs on the display.
To complete the Teach-in process, press and hold the Teach-in key for approx. two seconds until the green LED begins flashing rapidly. Release the Teach-in key. The LED is off!
Response Time
Switch the sensor to teach mode by pressing and holding the Teach-in key for approx. four seconds until the red LED begins flashing. Release the Teach-in key. The red LED lights up continuously. Press the Teach-in key repeatedly until the desired response time is achieved.
LED display:
no LED on; approximately 5 ms response time delay
1. LED on; approximately 10 ms response time delay
2. LED on; approximately 20 ms response time delay
3. LED on; approximately 40 ms response time delay
4. LED on; approximately 80 ms response time delay
5. LED on; approximately 160 ms response time delay
6. LED on; approximately 320 ms response time delay
To complete the Teach-in process, press and hold the Teach-in key for approx. two seconds until the red LED begins flashing rapidly. Release the Teach-in key. The response time is now set.
Ultrasonic distance sensors with qTeach
qTeach
The new, comfortable and wear-free qTeach teach method was developed and introduced by Baumer.
Teaching of O500 sensors is just by a touch with any ferromagnetic tool. A blue LED light provides clear optical feedback. To prevent user errors, qTeach locks autonomously after 5 minutes.
Adjustment with qTeach
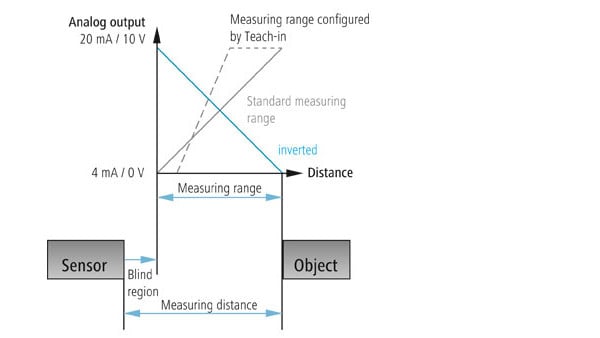
Adjustment of 0 ... 10 V output function
To switch the sensor into Teach mode, hold the Teach-in button for 2 seconds or more. Successful entry into Teach-mode is signaled by the flashing bicolor LED. Upon release of the Teach button the red LED will flash. Another press on the button will teach in the close limit (Sdc) which is followed by the far limit (Sde). The sensor LED lighting up for 2 seconds will confirm the completed teaching operation. At this point, you may set the close limit (Sdc) by placing the target at the required distance from the sensor (the closest the target will be to the sensor face) and briefly pushing the button or connecting the Teach-in wire with +VS. The LED will then flash Amber. Far limit (Sde) may now be programmed by placing the target at the farthest required distance from the sensor by briefly pressing the button or connecting the Teach-in wire with +VS. Both LEDs will be „on“ for 2 seconds to confirm proper completion of Teach-in process.
Programmable output curve
Optional on request
Separate digital PNP output with one switching point which may be set up using the Teach-in function.
Inverting the output function to 10 ... 0 V
Sensor output signal can be inverted to 10 ... 0 V by teaching the far limit Sde first and the sensor close limit Sdc second.
Linearity
Deviations in linearity are mainly generated within the sensor and by changes in ambient temperature. Resolution, temperature drift and repeatability define the linearity error.
Minimum load resistance
The voltage drop across the load resistance is proportional to the current, using a sensor with current output. To ensure a proper functioning of the output stage do not exceed the maximum permissible load resistance as stated in the data sheet.
Resolution
Defines the smallest position change of the object which causes a change in voltage or current at the sensor output.
Angular deflection
Function and technology of ultrasonic sensors
Ultrasonic sensors utilize ultrasonic waves to detect objects or measure distances. Find out more about the function of ultrasonic sensors.